Corporate Governance
Corporate Governance
Fujita Kanko aims to become a company that contributes to realizing a prosperous society through its business operations. Toward this end, the Company constantly works to fulfill its corporate governance to ensure a favorable relationship with all stakeholders, including shareholders, and to realize corporate social responsibility. The following are the Company's basic principles of corporate governance, which are reviewed on a continuous basis to further enhance corporate value.
General Provisions
(The Company's basic principles of corporate governance)
- The Company must always pursue the best possible corporate governance and dedicate itself to fulfilling it.
- Through corporate governance, the Company must strive to improve its long-term corporate value in accordance with the following principles.
(1) Relations with stakeholders (including shareholders)
- Must respect all shareholders’ rights.
- Must guarantee equality for all shareholders.
- Must build good relations with all stakeholders (including shareholders).
- Must release all important information in an appropriate way for transparency.
(2) Structure for corporate governance
- The Company must have a board of auditors.
- The Company must have impartial outside directors among the board of directors.
- The Company must include an internal audit department :Internal Audit Office.
Corporate Governance Framework
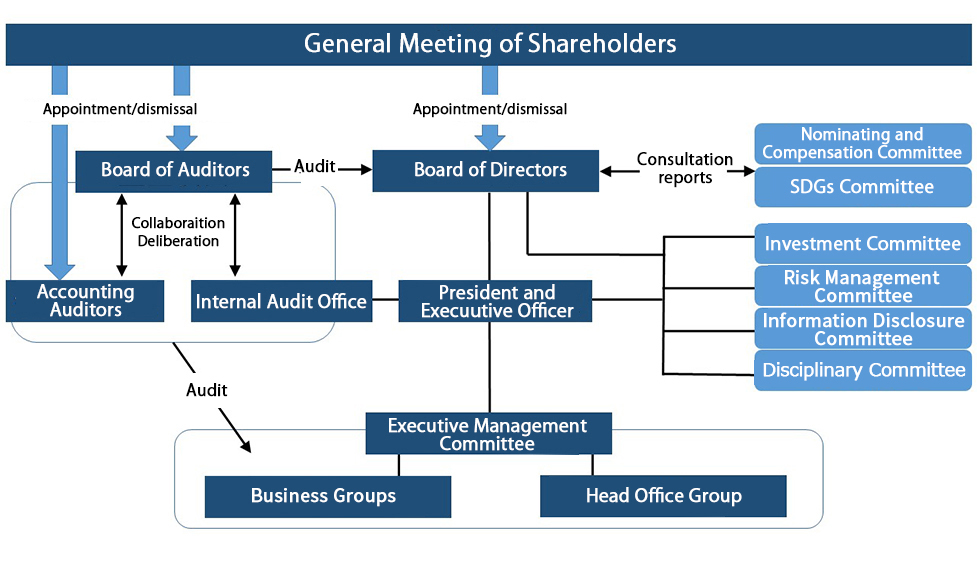
Ensuring Shareholder Rights and Equality
(Respecting the right of all shareholders to vote)
- The Company must properly uphold the right of shareholders to vote at the General Meeting of Shareholders.
- To ensure ample time for shareholders to examine each proposal at the ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders, the Company must place a notice of the meeting on its website and the Tokyo Stock Exchange website and send shareholders notification and reference documents 3 weeks before the meeting.
- The Company must provide an environment where not only shareholders who attend the General Meeting of Shareholders, but all shareholders can appropriately exercise their right to vote.
- To grasp shareholder opinions at the General Meeting of Shareholders, the Company must analyze and report the voting results of each proposal after each meeting.
(General Meeting of Shareholders)
- The Company must make efforts to reflect the opinions of shareholders who hold the right to vote at the General Meeting of Shareholders.
- The Company must try to establish a date and place for the General Meeting of Shareholders that enables more shareholders to attend and express their opinions.
- The director and executive director answering questions at the General Meeting of Shareholders must provide sufficient explanations and hear out the questions of shareholders.
(Ensuring shareholder equality)
- The Company must treat all shareholders equally in proportion to their share.
- The Company must refrain from granting special benefits to shareholders who own specific assets.
- The Company must release information in an appropriate and timely fashion to all shareholders so there is no information gap between them.
- The Company must establish rules and methods to handle shares and help minority shareholders smoothly exercise their rights, including inspection of the share register and minutes of the Board of Directors meetings and submission of proposals at the General Meeting of Shareholders.
(Returns to shareholders)
- Returns to shareholders must be determined after taking into account business performance and accumulated internal reserves for expanding and strengthening business operations.
(Policies on the exercise of voting rights regarding strategic shareholding and strategically held shares)
- For strategic shareholding purposes, the Company must limit its shareholdings in other companies to improve its corporate value, strengthen relations with business partners and build mutual trust with issuing companies. When the Company determines, following inspection of medium-and-long term economic potential, that specific stocks in its possession will not contribute to its corporate value, it must sell them gradually.
- As for the exercise of voting rights for strategically held shares, the Company must decide its votes by considering if a particular proposal ensures appropriate decision-making in keeping with improvement of the corporate value of issuing companies, if it helps improve the Company’s corporate value, etc.
Consideration of stakeholder profits
(Official code of ethics and conflict of interest)
- The Company must establish an official code of ethics at a Board of Directors meeting to help ensure the executive director and other directors behave ethically at all times.
- The Company must establish Rules for the Board of Directors (in a separate document) regarding reporting duties and approval for directors to become special interested persons.
(Relations with stakeholders)
- The Company, toward improving its long-term corporate value, must respect its diverse stakeholders (including shareholders) and try to maintain smooth, positive relationships with them.
Appropriate information disclosure and transparency
(Information disclosure)
- The Company must actively and appropriately disclose important company information to shareholders.
- The Company must establish an Information Disclosure Committee to oversee the release of information in accordance with legal standards.
Obligations of the Board of Directors
(Roles of the Board of Directors)
- The Board of Directors, while supervising the efficient and practical implementation of corporate governance in accordance with the Company's corporate philosophy, must strive to make fair judgements and effective decisions.
- The Board of Directors must make important management-related decisions in accordance with basic corporate policies, government laws and ordinances, the corporate charter and Rules for the Board of Directors.
- The Board of Directors must entrust business decision-making to the executive management team by establishing Approval Authority Regulations to energize management and make business administration more agile and flexible.
(Structure)
- The Board of Directors must be comprised of up to 12 members, including independent outside directors.
(Chairman of the Board of Directors)
- The chairman of the Board of Directors must be the representative director and president of the Company.
- The chairman of the Board of Directors must provide board members with the information necessary to deliberate on proposals at Board of Directors meetings.
- The chairman of the Board of Directors must administer Board of Directors meetings to promote active discussions on proposals.
(Qualifications and appointment standards)
- The Company must appoint each director following sufficient consideration of the candidate's personality and knowledge, as well as ability to perform required tasks, fulfill responsibilities including Duty of Care and Duty of Loyalty to the Company, and contribute to company growth and value regardless of gender, age or nationality.
- The Company must appoint each outside director in accordance with the standards of legal statutes and the Tokyo Stock Exchange following sufficient consideration of the candidate's ability to support monitoring and supervision of management through practical and objective advice backed by abundant experience and rich knowledge of management in general and fields of expertise.
[Qualifications for outside directors]
- 1. Must have no experience serving as a business executive for the Company or its subsidiaries.
- 2. Must not be one of the Company’s ten major shareholders, nor a major shareholder (or in the case of a corporation, an individual affiliated with it) holding 10% or more of the total voting rights either directly or indirectly.
- 3. Has not worked for an organization accounting for over 2% of Company or Group consolidated annual sales in the last three fiscal years.
- 4. Must not have received an average yearly compensation, or other financial benefits, from the Company worth over 10 million yen during the last three fiscal years (and does not currently work for a company in that capacity) as a consultant, accountant, legal expert, auditor or advisor.
- 5. If the person qualifies for point 2, 3 or 4 above, three years or more must have passed since resignation from said organization or company.
(Director compensation)
- The executive director’s compensation must be in proportion to performance.
- The ratio between basic compensation and performance-based compensation must be fair, balanced and designed to motivate directors to maximize company value and benefit stockholders in the long run.
(Nominating and Compensation Committee)
- With the aim of strengthening the independence, objectivity and transparency of the functions of the Board of Directors pertaining to the selection and dismissal of Directors and procedures for nominating candidates for Directors and Corporate Auditors, the Company must establish a Nominating and Compensation Committee, composed majority of outside Director, as an advisory body for the Board of Directors.
(Director responsibilities)
- The directors must assume fiduciary duties to shareholders and responsibilities to all stakeholders related to the Company and be committed to continually improve corporate value.
- To execute duties effectively, the directors must gather sufficient information and actively express opinions.
- Each director, upon assuming responsibilities, must fully understand his or her responsibilities by gaining full knowledge of related legal statutes, company rules, the Rules for the Board of Directors and other internal regulations.
(Board of Auditors)
- The Board of Auditors must audit directors concerning their execution of duties; decide which proposals will be presented at the General Meeting of Shareholders regarding the appointment, dismissal and reappointment of accounting auditors; carry out financial audits and conduct other matters stipulated by laws.
- The Board of Auditors must strive to improve audit quality and carry out effective audits on directors executing their duties by receiving reports from executives and employees in the Company's group companies and collaborating with an internal audit department.
- The Board of Auditors must arrange meetings with outside directors as needed to share opinions and better supervise executive directors.
(Director and auditor training)
- Directors and auditors must improve their own abilities to fulfill their responsibilities by actively and continually seeking information on the Company's finances and complying with laws and corporate governance principles.
- The Company must provide directors and auditors with opportunities to improve their abilities as needed. The Company must also provide opportunities for newly appointed directors and auditors to fill in any gaps in knowledge and abilities related to fulfilling their roles and duties.
Dialog with shareholders
(Dialog with shareholders)
- The Chairman of the Board of Directors must provide shareholders with ample information to share their opinions with all directors.
- The Company must establish separate basic IR policies to enhance dialog with all shareholders and help build a relationship of mutual trust.
- Policies
- IR Library
- Stocks